Cloud Adoption and Optimization: Embracing a Digital-First Strategy
The term “digital first” has popped up in recent years, describing a mindset that puts technologies at the core of businesses and their strategies. According to the International Data Corporation (IDC), 95% of organizations report that they are implementing a digital-first strategy to support new digital revenue streams. By 2027, the average enterprise will see 41% of revenue originating from digital products and services.
Fast-developing cloud technologies add fuel to the transition. Enterprises can now easily migrate services to the cloud and rapidly adopt various software with the Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) model. As seen in the European Data Centres Figures Q4 2023 by CBRE, the growing number of data centers reflects the demand for cloud services.
To realize a digital-first strategy, cloud service providers and transport network operators must be ready to enable a low latency, secure, and agile infrastructure. Here, we will analyze some important factors that can help enterprises implement a seamless digital-first business model.
Types of data centers
Traditionally, various types of data center configurations fulfilled different data processing demands based on their scale and performance requirements. Here are some typical data centers.
Hyperscale or cloud data center
These are owned and run by multi-national enterprises and offer services such as storage, computing, Software-as-a-Service (SaaS), and more to the public. They are designed to provide extensive workloads with large-scale IT infrastructure.
Colocation or multi-tenant data center
This describes providing facilities to enterprises that do not intend to build privately owned data centers. Tenants can pick the services relevant to them, from space only to a full set of IT infrastructure, as well as management and support services.
Edge or regional data center
Edge or regional data centers may be operated by network service providers, data center service providers, or individual enterprises. The purpose of edge or regional data centers is to bring the data closer to end users to minimize the response time.
Enterprise or on-premises data center
Enterprise or on-premises data centers are owned and operated by individual organizations, hosting their own IT infrastructure and providing private services within the organization.
The horizon starts to shift a little when we consider the AI era.
AI Training Data Center
AI training requires massive computing power and resources. As such, AI training data centers tend to be vast in size and owned by top-tier hyperscalers.
AI Inference data center
Inference describes a service intended to generate revenue from AI. It is smaller in scale and requires less computing resources. Individual organizations or data center service providers can build and run an AI inference data center close to the end user to shorten the response time.
The synergy of different types of data centers and high-performance transport networks provides a platform for enterprises to build optimized IT solutions. Enterprises that started with full public cloud structures are now conducting cloud repatriation to adopt a more flexible and secure hybrid cloud model by utilizing colocation services to host private cloud networks.
Inter- and intra-datacenter networks must meet the following requirements to provide the best user experience.
● Low latency interconnections
● Secure data transmissions
● Agile infrastructure
● Scalable topology
Low latency interconnections
Enterprises distribute services and data in multiple data centers. To streamline operations, the network from the data center to the enterprise and between data centers must ensure a low latency transportation.
The Innovative Optical and Wireless Network (IOWN) Global Forum works on new communication and network infrastructure technologies to enable a seamless communication experience, offering low power consumption, high bandwidth, and fast-responding networks. One of the ultimate goals is to deliver an all-optical end-to-end network through photonics-based technologies.
A mid-term solution to support the low latency infrastructure is IPoDWDM. With developed OpenZR+, the packet network and optical network can be collapsed into one domain. This brings cost benefits as well as network efficiency and simplicity. With fewer components between the two ends, data can run faster and the network topology can be simpler, helping to optimize the transport performance.

Figure 1 OpenZR+ enables a flexible and efficient optical transport network
Security concerns in the colocation data center
Security is one of the biggest concerns for enterprises when hosting servers and services off the premises. Every transaction goes through a public network, increasing the risk of data theft.
Data center service providers adopt multiple approaches to maintain transmission integrity. MACsec is one such mechanism, and offers a layer 2 data protection in line-rate. It provides point-to-point data encryption, meaning it must support MACsec at both ends. It can be deployed between the user's premises and the service provider’s edge router to protect the connection between these two sites, or inside the data center where the user's server resources tap into the shared network to ensure other entities do not see the transactions.
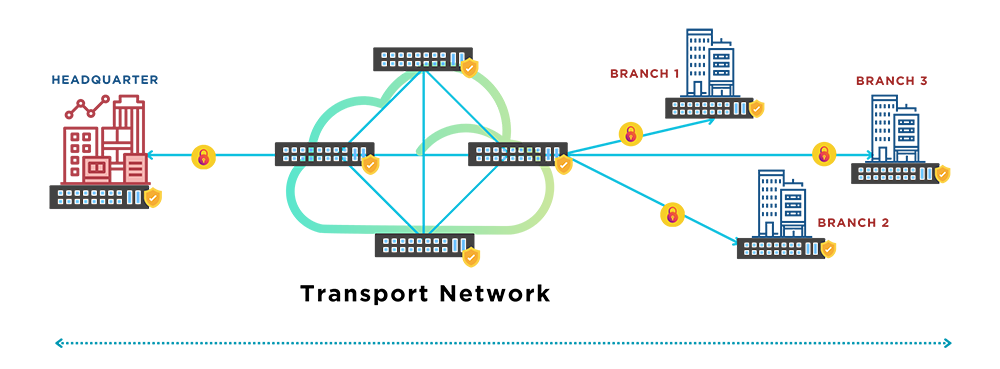
Figure 2 MACsec protects data transmission in line-rate
New demand features
Data center usage is changing with the development of AI, machine learning, and big data analysis. Enterprises may deploy AI-related solutions on the cloud, or utilize AI SaaS solutions from the cloud. Traffic patterns and networking requirements of AI services differ from those of traditional data centers, which is why many data center operators have started to deploy router solutions originally used in telecom networks. This leverages their deep buffer and programmability to optimize network performance and fulfill AI networking requirements.
Scalability
Data centers must be flexible on scale to answer the demands of diverse applications and traffic requirements. Spine-leaf architecture is the most common approach to building a flexible and scalable network fabric. It is designed to accommodate the east-west traffic demand inside traditional data centers and is easily deployable to fit into data centers of different scales.
Another popular approach is using a Distributed Disaggregated Chassis (DDC) solution. It leverages CLOS topology to build a virtual chassis with multiple white box routers. It has similar scalability as spine-leaf architecture and can be managed as one big router. The cell-switching mechanism utilizes internal connections and provides low latency and load-balanced data transmissions, making it suitable for AI and traditional data centers.
Takeaway
Both data centers and telecom infrastructure must be on board to adequately support a digital-first strategy. It requires low latency, secure interconnections, and agile and scalable infrastructure to provide the best user experience for enterprises to go to the cloud.
UfiSpace has a holistic product line and rich deployment usage cases to respond to the demand, including:
● A complete portfolio of data center switches covering 1G~400G speed requirements.
● Next-generation 800G routers and switches for coming AI data booms.
● End-to-end transport network solutions with OpenZR+ support, helping operators build high-efficiency and cost-effective optical transport networks.
● Complete solutions with MACsec support for transport security.
● Field-proven solutions to deploy Broadcom Qumran-based platforms into data centers to fulfill new traffic demands.
● We are leaders in DDC development, helping operators to optimize existing networks and explore new application scenarios.
Contact us to find out more about our offerings.
About the Author
 |
Will Chang Will Chang, Technical Marketing Manager at UfiSpace, provides technical expertise and executes marketing campaigns on technical topics. |
