Disaggregating the Broadband Network Gateway
by Will Chang

With our recent announcement of joining Telecom Infra Project's (TIP's) OpenBNG initiative, it only seems right that we take a look into what a BNG is and explore the potential benefits of OpenBNG. So, we’ll take a look at the OpenBNG specifications (referencing TIP OpenBNG - Technical Requirements v1.0), highlight some major points and explain some things along the way.
What is Broadband Network Gateway?
When broadband subscribers want to connect to the broadband network, they need to gain access through a Broadband Network Gateway (BNG). A BNG establishes and manages subscriber sessions, by aggregating traffic from multiple subscriber sessions and routing it to the network of the service provider.
In the past, the BNG didn’t do any routing, its main purpose was to manage subscribers’ access using functions such as:
- Authentication, authorization and accounting of subscriber sessions (AAA)
- Address assignment
- Security
- Policy management
- Quality of Service (QoS)
However, with the advancement of routers, now a BNG can integrated within an aggregation router to perform AAA of subscriber sessions and routing within the same device. Nowadays, if you’re going to get a BNG, you can bet it’ll be within a router.
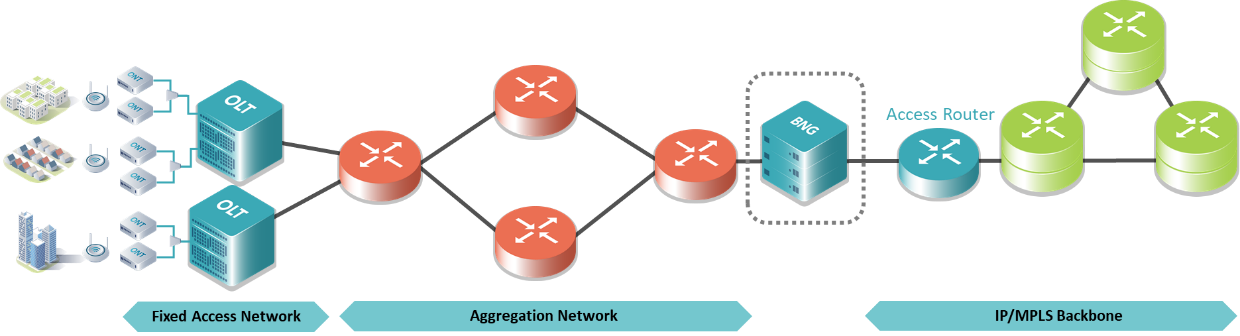
Based on TIP OpenBNG - Technical Requirements v1.0
A typical BNG network architecture is shown above. The Customer Premise Equipment (CPE) manages services such as phones, TV and computers, which are aggregated together at the fixed access network, then passed through the aggregation network to the BNG for session management. Those that can access the broadband network are routed through to the core network.
What are the challenges of the current BNG?
Consumer trends are changing more than ever before. Customers are more demanding than ever for more services in real time and at lower costs. New competitors are entering the market with new fiber networks without the need to maintain older copper networks. For a broadband network operator, the need for faster deployment, lower costs and ease of integrating new services has begun to push the limits of what traditional BNG routers can do.
Monolithic BNG platforms make it difficult to introduce innovations from other venders and the lack of openness can lead to:
- Limited hardware selection for software integration
- Limited feature extensibility for software
- Lack of interaction between a device and external components
A more modular approach to AAA services is needed in order to provide faster and more cost effective services to subscribers. Additionally, by adopting an open disaggregated architecture additional benefits can be achieved such as:
- Standardized features and tools for ZTP (Zero Touch Provisioning) and initial auto-configuration
- Reduce costs for system integration and faster time to market for new solutions
- Break out of vendor lock-in
- Enable an ecosystem of vendors for developing solutions and services
What is OpenBNG?
OpenBNG is an initiative that was set forth by the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) to facilitate the migration of BNG toward a disaggregated and standards-based architecture.
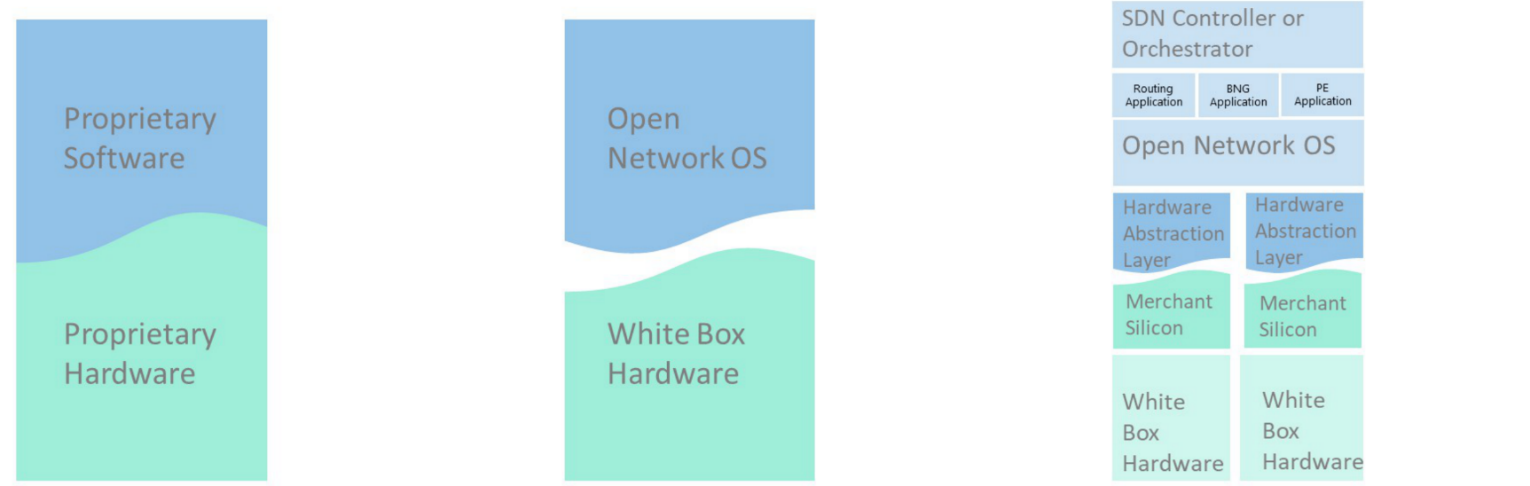
The first step is to disaggregate the monolithic BNG platform into hardware and software components, built with commercial silicon. The BNG hardware provides open and programmable interfaces, which allows different NOS software to run on top of it.
The second step is disaggregating the software. A base operating system is in charge of resource coordination and communications with the hardware through a Hardware Abstraction Layer (HAL). Different software packages could be installed to offer different functionalities to accommodate the different roles a BNG box could take within the network topology.
Through the North Bound Interface (NBI), the control plane is separated from the data plane. An SDN controller will oversee the whole network and manage each BNG box to handle the subscriber’s traffic in a smarter and more efficient way.
Based on the principles of disaggregation, TIP defines two roles and three deployment scenarios to cover all BNG use cases.
Two roles of OpenBNG:
- Full functionality BNG: Other than typical BNG features, it will also include the aggregation function and aggregates traffic from enterprise and mobile backhaul.
- Service-only BNG: Performs purely BNG services, not inline with the aggregation network.
Three scenarios of OpenBNG:
- Distributed: Deployed close to users with smaller scale of service capacity. Subscribers volume is up to 32k.
- Medium distributed: Generally deployed in a regional Point of Presence (PoP) and subscribers scale up to 128k.
- Centralized: Centralized BNG service located in core. The subscribers scale beyond 128k.
We will touch the detail of roles and scenarios later on.
What are the benefits of Open BNG?
OpenBNG aims for providing a holistic, flexible and economic approach to help service providers build the BNG service. Here we highlight just some of the benefits of OpenBNG.
- With hardware and software disaggregation, it encourages innovation and fosters the development of new solutions.
- The disaggregated architecture also brings more flexibility for deployments. The feature set and requirement vary in different types of deployment scenarios, service providers could select optimized configuration on demand.
- Standards-based designs eliminate interoperability concerns. Third party software could easily fit in to provide extra services such as automation, provision and management.
- A complement to the Broadband forum TR-459 (Control and User Plane Separation for a disaggregated BNG), which only defined Control Plane & User Plane separation but not hardware & software disaggregation.
Open BNG Scenarios proposed by Telecom Infra Project
The Telecom Infra Project has written three types of use case scenarios for the OpenBNG. The scenarios vary in the position it is placed within the network plus the features required for fulfilling that position. Below we will give an overview of each scenario.
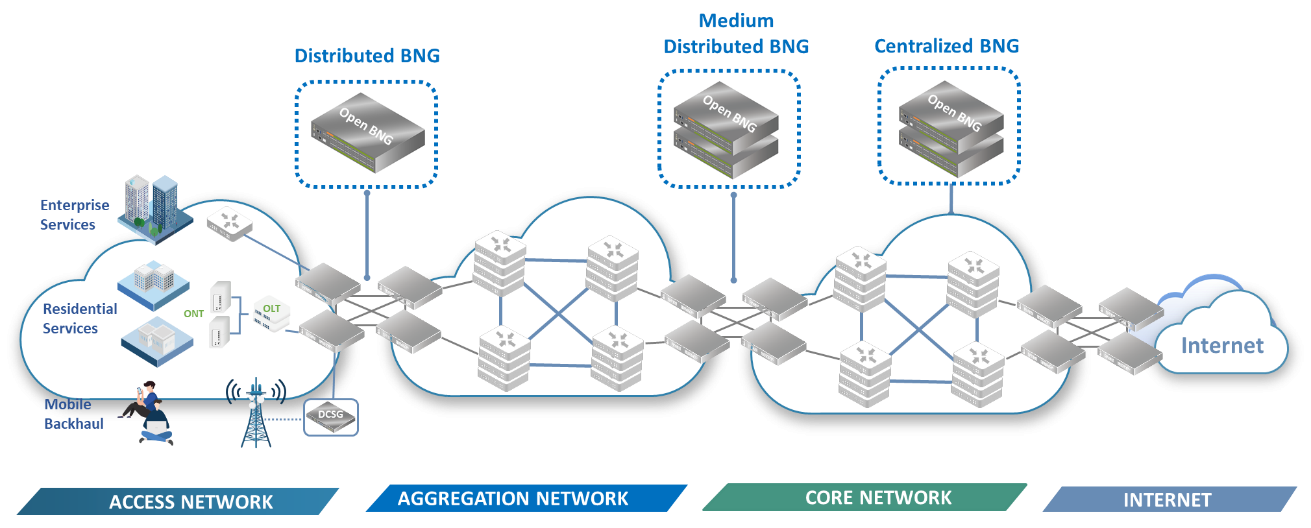
Based on TIP OpenBNG - Technical Requirements v1.0
Full Functionality and Distributed Requirement
Let’s break this down starting with what is meant by “maximum distribution.” The more distributed the BNG is the closer it is positioned to the customer. So maximum distribution in this sense will be a BNG positioned as close to the customer as can be. It will be the first line aggregation point for traffic coming from mobile backhaul, fixed access, and enterprise devices.
This leads to the need for full functionality. The OpenBNG will need to deal with VLANs towards the access network, routing requirements towards the mobile backhaul/aggregation network, and acts as a PE for the enterprise VPN services. Naturally, the OpenBNG will also need to meet the time synchronization requirements for mobile backhaul.
Full Functionality and Medium Distributed Requirement
This scenario is almost the same as the Full Functionality and Distributed OpenBNG with the exception of the location in which it will be installed. Being less distributed, in a “medium location”, this OpenBNG will be positioned further down the aggregation line. Therefore, it will need to aggregate more subscribers than the distributed scenario. More 100GE ports may be needed here to cover growing traffic demand of wholesale service or mobile network.
Service Only and Medium Distributed/Centralized Requirement
The third scenario is more geared towards the BNG positioned as a node at central locations and not as an integral part of the aggregation network. Since it’s not in line with the aggregation network, time/phase synchronization support for mobile backhaul isn’t needed. This type of BNG will instead pass the timing synchronization through to the aggregation network. The subscriber’s volume may scale beyond 128K, so multiple devices or a spine-leaf cluster could be adopted here.
UfiSpace's solutions for Open BNG
UfiSpace is working with several NOS partners to develop open aggregation routers to cover all the TIP Open BNG configurations. All of the solutions have timing feature support, with the capability to be positioned in the aggregation network to propagate synchronization signals.
UfiSpace offers three flavors of open aggregation routers that meets the requirements put forth by TIP for Open BNG. Visit our product page and check out our S9600 series for more details about all our aggregation router available.
Stay tuned for more updates by joining our Linkedin.

