What is a Distributed Disaggregated Backbone Router?
by Andrew Lui

Early last year, the Telecom Infra Project (TIP) announced a key milestone in their journey to disaggregate the transport network. With the support of major service providers such as KDDI, Vodafone, MTN and Telefonica, TIP released the technical specifications for their open IP/MPLS router the Distributed Disaggregated Backbone Router (DDBR). The DDBR can be used to expand the capabilities of current and future IP core backbone and peering networks.
It is less than a year later and TIP has announced their shortlist for their DDBR RFI, with UfiSpace being selected as one of the solution providers along with DriveNets. I have to say it is an honor to be a part of such a game changing project, but for those who are not aware of what the DDBR project and how it can bring value to service providers, here's a little background.
What is a Distributed Disaggregated Backbone Router?
The DDBR is a disaggregated open router that is used within a system architecture for the service provider IP backbone, sometimes referred to as the core network, which is a national or regional network that routes mobile and broadband traffic between their access networks or to external networks.
The DDBRs used in this type of backbone routing system are interconnected in a CLOS architecture consisting of line card white boxes and fabric white boxes. Together these components can create backbone router clusters of varying capacities ranging from 4Tbps up to 691Tbps. Since the DDBR is an interconnected cluster, the capacity of the IP backbone can be increased, if and when it's needed, by adding on additional boxes. So essentially, a service provider looking to disaggregate their IP backbone can start with a cluster that meets their current demands and increase its capacity as demand increases, making it easier for them to plan for, invest in and upgrade their core networks.
DDBRs are integrated with a central controller running on x86 servers or as a cloud native container. The centralized control plane brings benefits such as high compute scalability and efficiently implementing virtual network functions. Managing disaggregated white boxes this way breaks through some of the bottlenecks brought forth by traditional IP backbone systems for scalability such as control plane performance, capacity, and power consumption.
UfiSpace's Contributions to the DDBR RFI
UfiSpace has been one of the earliest contributors to TIP with our S9700 Series as disaggregated open routers. For the DDBR RFI, we proposed our S9700-53DX (high density 100G core router), S9700-23D (low density 400G core router), S9710-76D (high density 400G core router), and our S9705-48D (400G fabric switch). These UfiSpace routers will be part of the DDBR data plane, which consists of fabric white box acting as the backplane and packet forwarder white box acting as line cards.
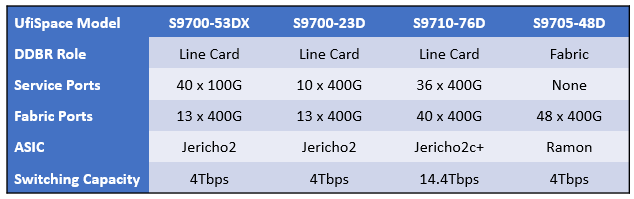
UfiSpace's Backbone Router Specifications
What's Next for DDBR?
With the DDBR RFI shortlist announcement completed, the next steps for TIP would most likely by testing and validation. Then once that's done, it'll be on to market trials.
For more information about our DDBR, please contact our sales team.
