What is Private 5G - Benefits, Architectures, and Requirements
by Will Chang

A private 5G network offers high bandwidth, low latency, and massive connections that are suitable for more business oriented applications. Compared with public networks, private networks are highly customizable. With so many requirements across industries, a private 5G transport network must be just as flexible to ensure the quality of service and maximize the value for the private network’s owner.
According to Dell’Oro Group, 5G will surpass LTE for the preferred technology of choice in private networks by 2026. This certainly makes sense seeing the key features brought by 5G, so let’s take a look at why 5G is so suitable for private 5G, the different types of private 5G architectures and the requirements it has for the mobile transport network.
Private 5G Emphasizes on Service and Flexibility
Most people are familiar with the functional enhancement brought by 5G. From an application perspective: eMBB (Enhanced Mobile Broadband) provides ultra-high speed for live streaming or AR/VR experience, uRLLC (Ultra Reliable Low Latency Communication) enables mission critical application, autonomous driving or manufacturing automation, and mMTC (Massive Machine Type Communication) allows large quantity of connections suitable for IoT scenarios or smart city deployment. However, there is something more with the very core design of 5G that makes it very suitable for private networks. That is, the 5G architecture is designed with two major concepts that help construct a flexible network:
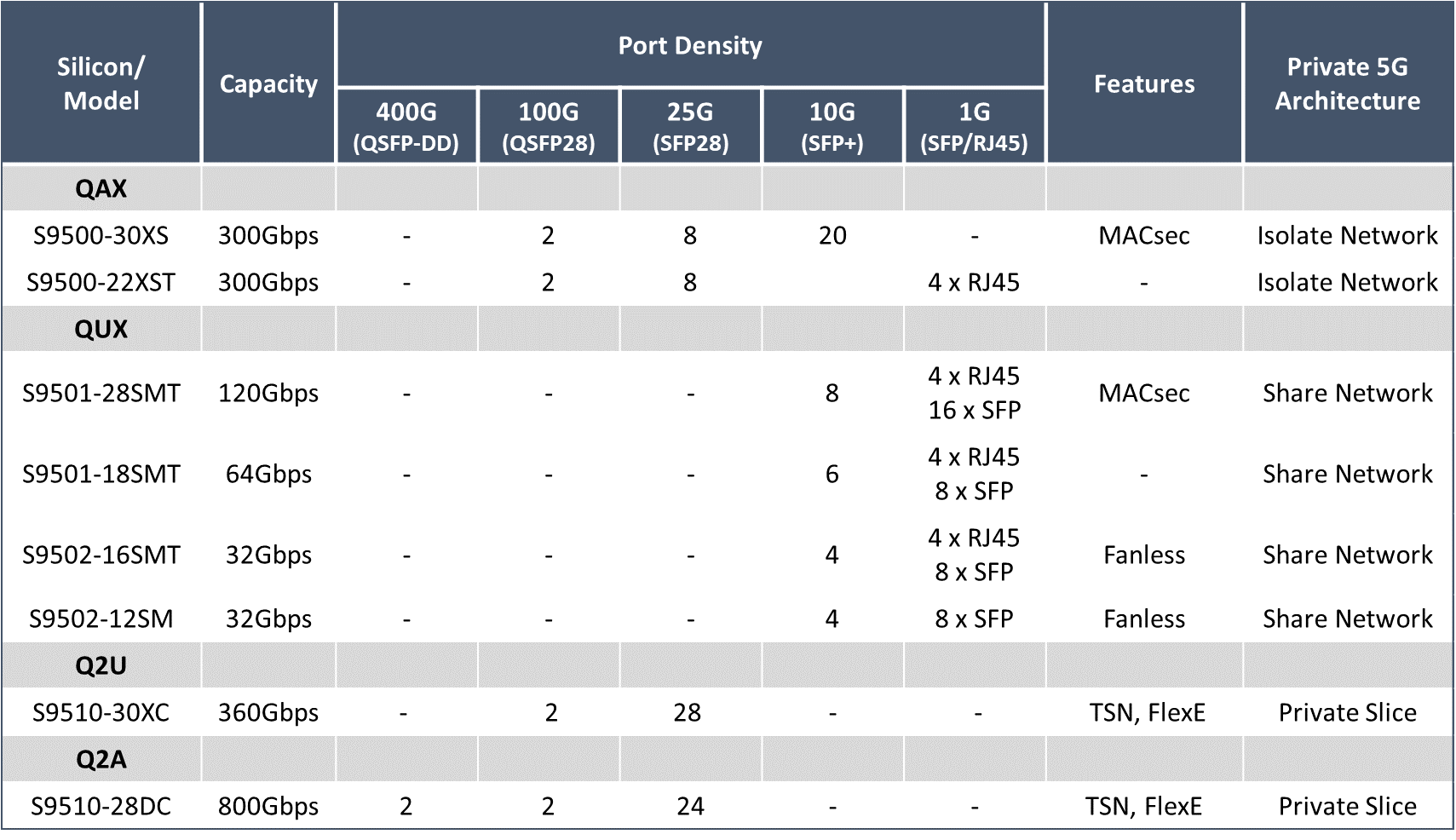
1. 5G uses a Service Based Architecture (SBA)
2. Control and User Plane Separation (CUPS)
5G built with SBA and CUPS architecture
Service Based Architecture
A Service Based Architecture is used broadly in software design to enhance system modularity. The system can be disaggregated into individual components and communicate via standard API. The 3GPP reorganized the network service into individual services called Network Functions (NFs). Each NF has a specific function and communicates with each other through a Service Based Interface (SBI).
Network functions interwork with each other and build up the 5G system. They are responsible for the operation of mobile networks such as authentication, IP address allocation, policy control, and user data management. The Service Based Architecture makes the 5G system very flexible and can integrate new services and applications for any industry demand.
Control and User Plane Separation
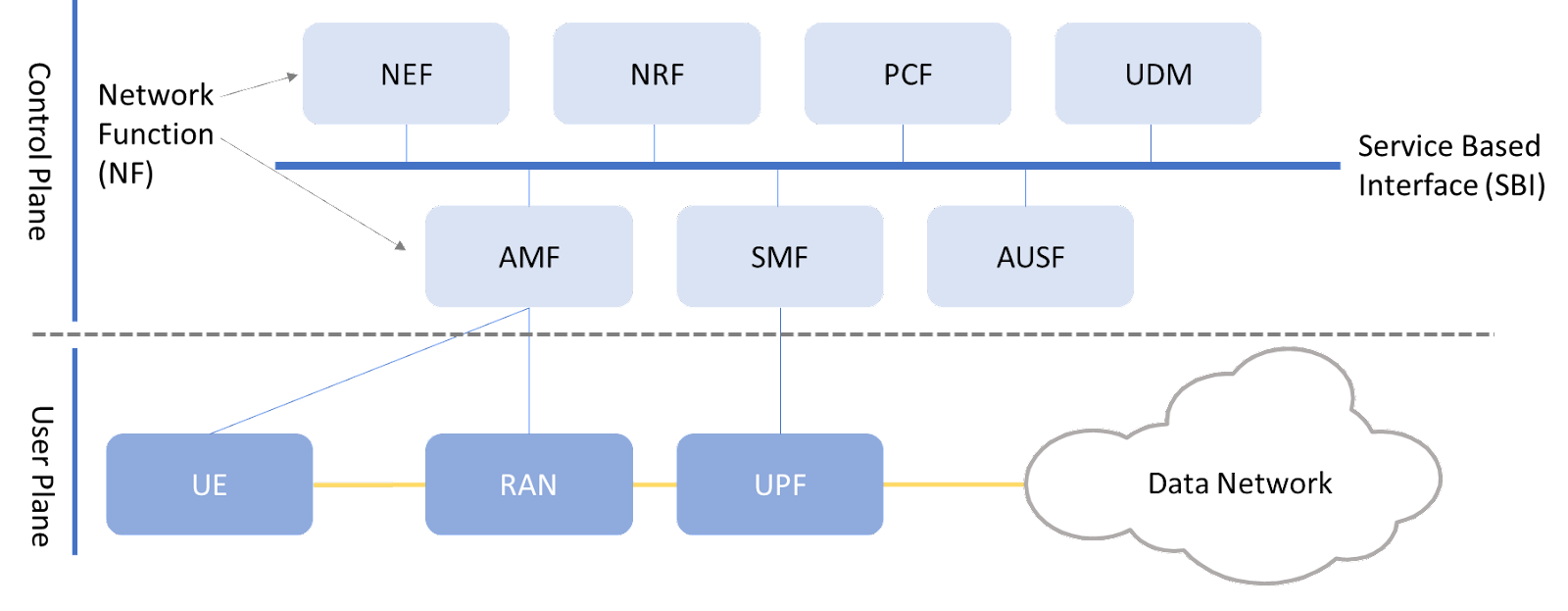
5G architecture is designed with Control and User Plane Separation, which allows operators to separate the 5G control function from the data forwarding function. The control plane could be deployed centrally while user plane function (UPF) could be deployed flexibly at any location of the network to accommodate to the different requirement on data processing.
UPF steers traffic and facilitate MEC deployment
SBA and CUPS offer great flexibility for mobile network design and implementation. It also helps to integrate MEC seamlessly into the 5G network. Edge computing service could interact with 5G core through SBA architecture and the service could be deployed in the appropriate location with UPF to steer the traffic to designate computing resources.
Now that we know what makes private 5G a suitable choice for private networks, let’s take a look at the different deployment scenarios for private 5G.
Private 5G Architectures
The private 5G network architecture can be deployed in multiple ways, but we can simply categorize the different deployment options with the level of integration with the mobile operator’s public network. Doing that, we come up with the following private 5G architectures:
• Isolated network - The entire private network is owned and operated by the user and completely isolated from the public network.
• Shared network - A hybrid configuration that leverage part of the telecom service provider’s infrastructure.
• Private network slice under public network - The private network is realized by network slicing. Leverage operator’s existing public network infrastructure and offer private connection through the software defined network slice.
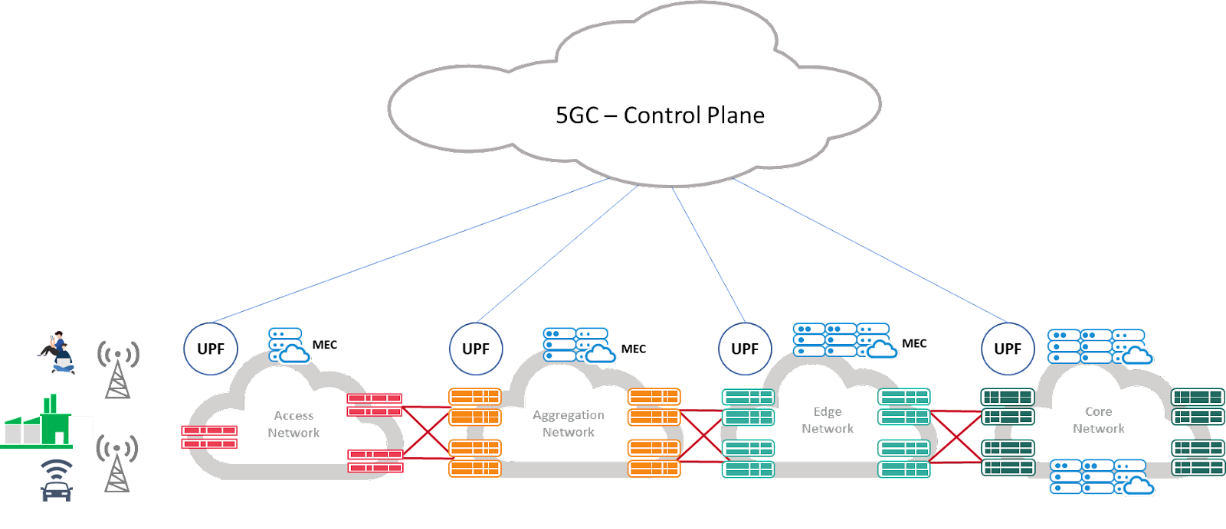
1. Isolated Private 5G Network Architecture
In an isolated private 5G network architecture, the entire network is hosted and operated by the user to ensure full control of the network. The network is completely isolated from public network, which minimizes the risk of data breach. The drawback is that the investment of building and operating the infrastructure is very high and will require personnel with a high level of knowledge about telecom networks.
Isolated 5G Private Network
With that being said, the isolated private 5G network is suitable for public safety agencies or large enterprises with an abundance of resources and high concern for data privacy. For example, public communication systems can be maintained for the rescue teams with an isolated private 5G network set up in a mobile vehicle.
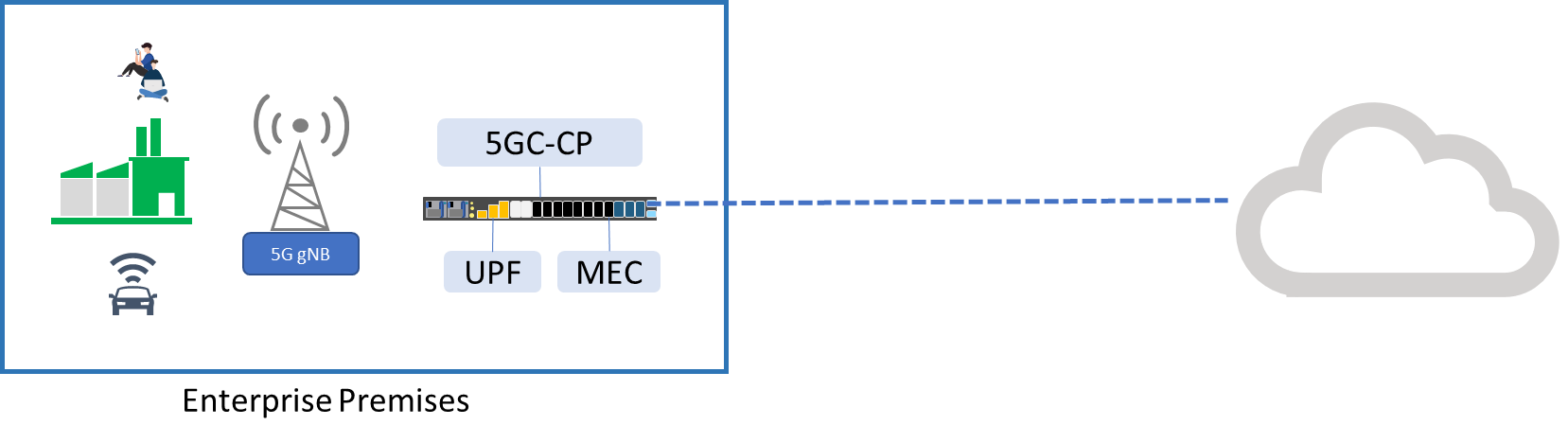
2. Shared Private 5G Network Architecture
A shared private 5G network architecture shares the infrastructure of a mobile operator’s public network to lower the cost of setup for the private 5G network. Depending on the business requirement, the user can choose how much components will be managed by themselves versus by the mobile operator.
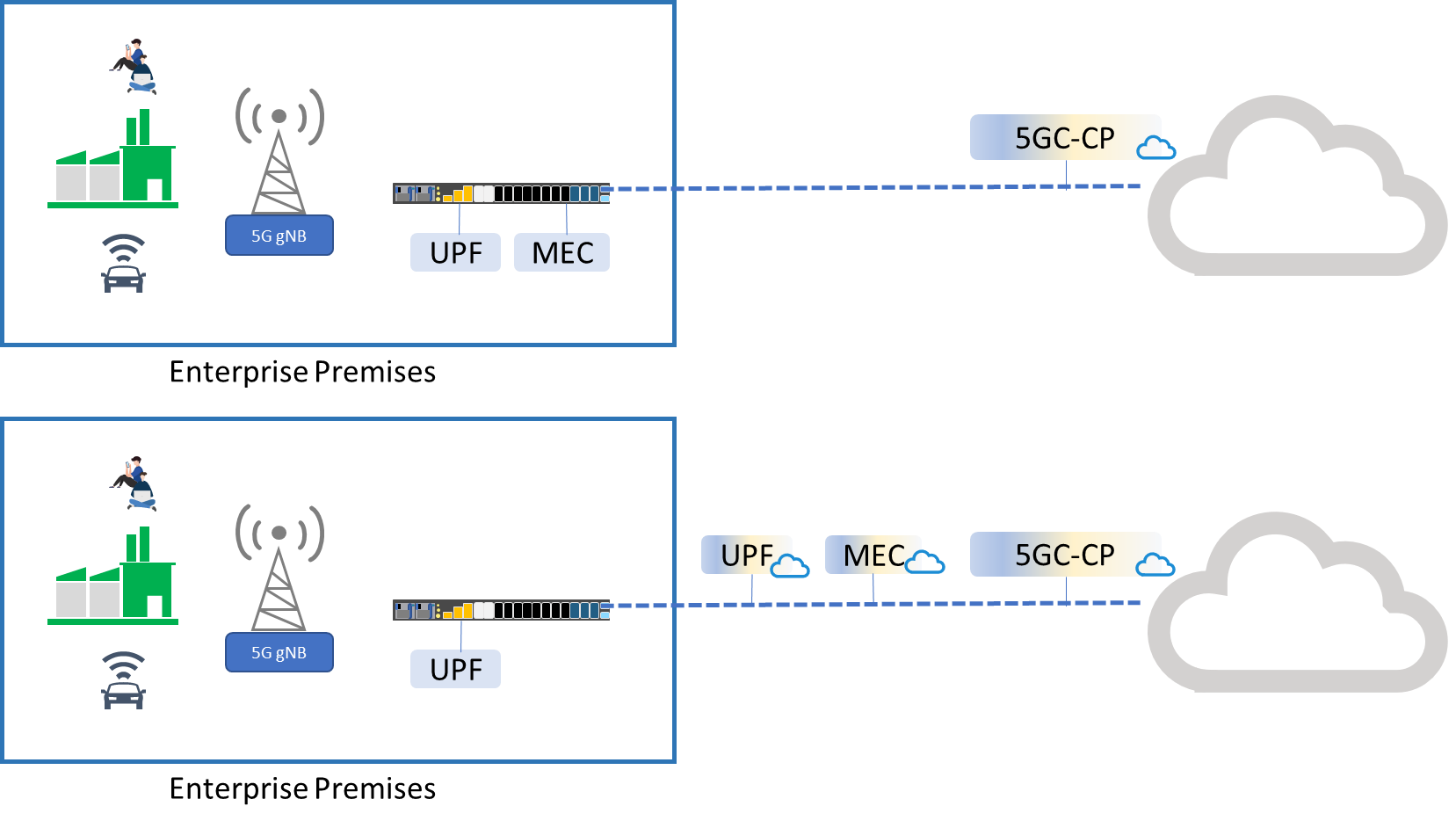
Shared 5G Private Network
In the case of a smart factory, it may be better to leave the MEC and UPF on premises. This allows for a private 5G architecture where the user can get low latency communication with room for future modifications.
For other types of use case scenarios such as stadiums or exhibition centers, where a fast and stable connection is needed, the business owner can maintain the RAN locally. This ensures that the coverage and network quality is under control while leaving the rest to system management to the mobile operator.
3. Network Slicing Private 5G Architecture
Network slicing can ensure data isolation and network quality when using an end-to-end private 5G connection provided by a mobile operator’s existing infrastructure. This approach has lowest investment cost for infrastructure, but it lacks control for the network.
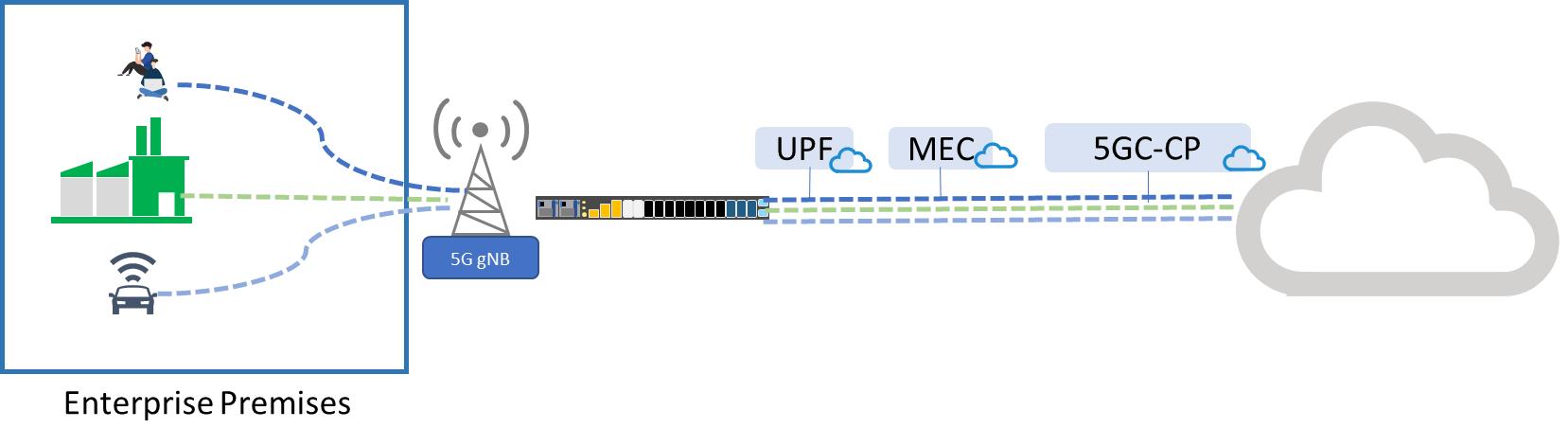
Private 5G Slicing Under Public Network
The network slicing private 5G network architecture suitable for scenarios that require deployment on wide area, such as smart city IoT connections or autonomous driving services. Organizations can lease a private bandwidth from the operator and depending on the business type, they can choose different Service Level Agreements (SLAs) to fit their business needs.
Private 5G Requirements for Transport Network
The flexibility needed within the private 5G architecture is also reflected in its transport network as well. For example, if we consider the three private 5G architectures above, each one will require a different types of transport equipment features to support it. In the isolated private 5G network architecture, a switch with a large enough port count is needed to interconnect all the components on the enterprise premises. In a shared private 5G network, a lower port count switch can be used or even use fanless designs to reduce noise in the offices. On the mobile operator’s side, for the network slicing 5G architecture, a high capacity FlexE enabled switch can offer network slicing through hardware and handle traffic from multiple tenants together with its public traffic.
Other than port counts and network capacity, in each private 5G architecture type, users should consider the following factors when choosing their private 5G network transport equipment.
Timing Support: Proper timing synchronization within the private 5G network will provide better performance and reduce the occurrence of dropped calls or hung data sessions. 5G also has more stringent timing requirements in the access the closer we get to the edge, so additional Time Sensitive Network features may be needed for more time critical applications.
Security: Multiple layers of data protection is essential to make sure sensitive data is not leaked outside of the company. Additional security can come with software level protection such as IPsec or hardware level with MACsec.
Functionality and Flexibility: With the abundance of potential use cases with private 5G, it is important that the transport network is able to maximize the quality of service for the network. Transport network equipment should have enough buffers, QoS functionality, and flexible connectivity to connect to the needed RAN components.
Selecting the right transport network equipment to maximize your private 5G network service can be made easier with UfiSpace’s S9500 Series of open access switches. UfiSpace is a leader in timing design and supports open networking standards capable of implementing any solution provider’s software.
With complete solution options to support different port configurations, switching capacities, MACsec, FlexE and more, our switch portfolio covers all scenarios needed for private 5G implementation. For more information or get samples of our private 5G switches, please contact our sales team.